$80.09
Testosterone enanthate is a potent and effective form of testosterone used for its muscle-building and performance-enhancing properties. While it offers benefits in terms of muscle growth and athletic performance, users should be aware of the associated risks and side effects. Responsible use under medical supervision and adherence to legal and ethical considerations are crucial for anyone considering the use of testosterone enanthate or any other anabolic steroid.
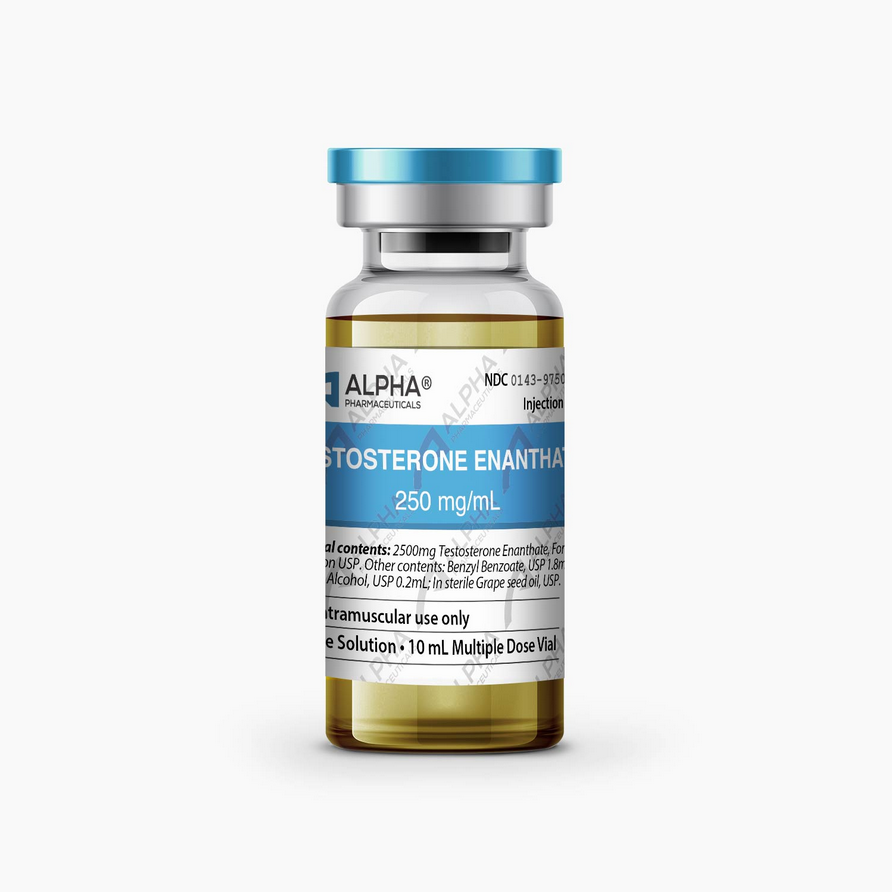
Testosterone enanthate, often referred to simply as “test enanthate,” is a long-acting ester of testosterone. It is one of the most commonly used forms of testosterone in both medical and non-medical settings, particularly in the realm of bodybuilding and athletic performance enhancement.
Characteristics
- Chemical Structure: Testosterone enanthate is a synthetic derivative of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. It is structurally identical to the testosterone produced naturally in the body.
- Ester Attachment: Testosterone enanthate is attached to the enanthate ester, which slows its release into the bloodstream. This results in a prolonged half-life of approximately 4.5 to 5 days, allowing for less frequent injections compared to shorter-acting testosterone esters like testosterone propionate.
Uses and Benefits
- Muscle Growth: Testosterone enanthate promotes protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass and strength gains. It is highly effective in enhancing nitrogen retention and promoting muscle tissue growth.
- Performance Enhancement: Athletes and bodybuilders use testosterone enanthate to improve athletic performance, including increased endurance, power, and recovery between workouts.
- Medical Uses: In medical settings, testosterone enanthate is prescribed to treat conditions such as hypogonadism (low testosterone levels), delayed puberty in males, and certain types of breast cancer in women.
Administration
Testosterone enanthate is typically administered via intramuscular injection into the gluteal muscle. Due to its longer-acting nature, injections are usually required less frequently compared to shorter-acting esters like testosterone propionate. Typically, injections are administered once every 1 to 2 weeks to maintain stable blood levels.
Side Effects
While testosterone enanthate offers significant benefits, it also carries potential side effects, including:
- Estrogenic Effects: Testosterone can convert to estrogen in the body, leading to side effects such as water retention, gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement in males), and potential mood swings.
- Androgenic Effects: Testosterone enanthate can cause oily skin, acne, and accelerated hair loss in individuals predisposed to male pattern baldness.
- Cardiovascular Risks: Elevated testosterone levels may negatively impact cholesterol levels, potentially increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Suppression of Natural Testosterone Production: Like other forms of exogenous testosterone, testosterone enanthate can suppress the body’s natural testosterone production. Post-cycle therapy (PCT) is often used to help restore natural hormone levels after discontinuation.
Legality and Ethics
The use of testosterone enanthate, like other anabolic steroids, is regulated and controlled in many countries due to its potential for misuse and abuse. In sports, the use of testosterone enanthate is typically prohibited by anti-doping agencies and can result in sanctions and disqualification if detected during drug testing.
2 reviews for Test Enanthate
There are no reviews yet.
Related products
Injectable
Injectable

Be the first to review “Test Enanthate”